
Mon - Sat 9:00 - 17:30

Understanding ERPG: A Vital Tool for Emergency Responders
When hazardous chemicals are accidentally released into the air, time, information, and clear action plans can make the difference between a contained event and a disaster.
One of the most important tools for such planning is the Emergency Response Planning Guideline (ERPG) — a set of exposure limits developed by the American Industrial Hygiene Association (AIHA).
The Emergency Response Planning Guideline values represent airborne concentrations of chemicals for up to one hour of exposure that are expected to cause specific levels of health effects.
They help emergency planners, HAZMAT teams, fire services, and industrial safety officers decide when to evacuate, shelter-in-place, or take other protective actions.
| ERPG Level | Definition |
|---|---|
| ERPG-1 | The maximum airborne concentration below which nearly all individuals could be exposed for up to 1 hour without experiencing more than mild, transient health effects or odor-related discomfort. |
| ERPG-2 | The maximum airborne concentration below which nearly all individuals could be exposed for up to 1 hour without experiencing irreversible or other serious health effects, or symptoms that could impair their ability to take protective action. |
| ERPG-3 | The maximum airborne concentration below which nearly all individuals could be exposed for up to 1 hour without experiencing or developing life-threatening health effects. |
| Chemical | ERPG-1 (ppm) | ERPG-2 (ppm) | ERPG-3 (ppm) | Hazard Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonia | 25 | 150 | 750 | Corrosive to eyes and lungs |
| Chlorine | 0.5 | 3 | 20 | Strong respiratory irritant |
| Hydrogen Sulfide (H₂S) | 0.1 | 15 | 50 | Olfactory fatigue possible |
| Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂) | 0.3 | 3 | 30 | Causes choking sensation |
| Carbon Monoxide (CO) | 200 | 350 | 500 | Colorless, odorless, toxic |
| Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN) | 2 | 10 | 25 | Highly toxic, rapid onset |
| Formaldehyde | 0.1 | 1 | 10 | Sensitizer, irritant |
| Parameter | ERPG | AEGL | IDLH |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Emergency Response Planning Guideline | Acute Exposure Guideline Levels | Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health |
| Agency | AIHA | US EPA | NIOSH |
| Purpose | Community & industrial emergency planning | Public health protection, including sensitive groups | Worker safety & confined space entry |
| Exposure Duration | 1 hour | 10 minutes to 8 hours | 30 minutes |
| Tiers | 3 levels (ERPG-1, -2, -3) | 3 levels (AEGL-1, -2, -3) | Single value |
| Scope | General population | General population | Occupational |
| Key Use | Evacuation/shelter decisions | Environmental & public safety decisions | Respirator selection & work safety limits |
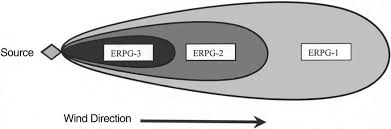
ERPG values help define protective action zones during chemical incidents.
ERPG-2 is often the trigger for evacuation or shelter-in-place orders.
ERPG-3 indicates immediate danger to life and requires urgent intervention.
Knowing how ERPG relates to AEGL and IDLH ensures coordinated action between emergency services and industry safety teams.
✅ To train your crew on ERPG, AEGL, IDLH interpretation or to carry out a site-specific chemical dispersion analysis, contact us at agnirakshaniti@gmail.com.
We can help ensure your team is prepared to respond quickly, safely, and effectively in any hazardous release scenario.