
Mon - Sat 9:00 - 17:30

CO₂ Flooding System – A Complete Guide
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) flooding systems are one of the most widely used clean agent fire suppression solutions for protecting high-value assets and critical equipment where water or foam is not suitable. These systems use CO₂ gas to quickly displace oxygen, interrupting the combustion process and extinguishing the fire.
Chemical Formula: CO₂ (Carbon Dioxide)
Color & Odor: Colorless, odorless in pure form (slight sharp odor in high concentration)
Density: 1.53 times heavier than air – ensures it settles and blankets the hazard
State in Cylinders: Stored as liquefied gas under pressure
Non-Conductive: Safe for energized electrical equipment
Non-Corrosive & No Residue: Leaves no clean-up requirement after discharge
Extinguishing Mechanism: Reduces oxygen concentration below the combustion threshold (typically <15%) and provides some cooling effect
Caution: Can cause asphyxiation at high concentrations – pre-discharge alarms and time delays are mandatory for personnel safety.
CO₂ systems are commonly applied in:
Electrical switchgear rooms
Generator rooms
Turbine enclosures
Paint spray booths
Engine test cells
Marine engine rooms
Industrial process equipment
Archives and document storage
Flammable liquid storage and handling areas
Key advantage: No residue, non-conductive, rapid fire knockdown.
Total Flooding System
Protects an entire enclosed area by discharging CO₂ to achieve an extinguishing concentration throughout the volume.
Used in enclosed machinery spaces, control rooms, etc.
Local Application System
Directs CO₂ only to the fire hazard area, without flooding the entire room.
Suitable for open hazards like dip tanks, conveyor belts, or flammable liquid filling points.
| Parameter | High-Pressure CO₂ System | Low-Pressure CO₂ System |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Pressure | ~58 bar at 21°C | ~21 bar at -18°C |
| Storage Method | Individual steel cylinders (typically 45–68 kg each) | Large refrigerated storage tank |
| Temperature Control | Not required (ambient) | Refrigeration unit maintains liquid state |
| Space Requirement | More space for multiple cylinders | Compact for large quantities |
| Typical Applications | Small to medium hazards | Large hazards requiring massive CO₂ volume |
| Discharge Time | Rapid | Rapid |
| Maintenance | Easier – individual cylinder checks | Requires refrigeration system upkeep |
| Cost | Lower initial cost for small projects | Economical for very large systems |
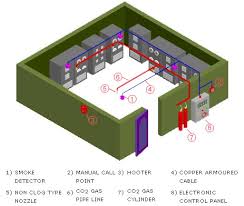
CO₂ Storage (Cylinders or Tank)
Discharge Nozzles
Manifold and Piping Network
Control Panel
Release Mechanism (electric, pneumatic, or manual)
Time Delay Device
Warning Alarms & Flashing Beacons
Manual Pull Stations
Safety Interlocks (ventilation shutdown, dampers, machinery stop)
| Fuel / Hazard | CO₂ Concentration (%) | Flooding Factor (kg/m³) |
|---|---|---|
| Flammable Liquids (Class B) | 34–40% | 1.1 – 1.2 |
| Electrical Hazards | 34–38% | 1.0 – 1.1 |
| Surface Fires (Class A) | 50–55% | 1.4 – 1.6 |
| Deep-Seated Fires | 55–65% | 1.6 – 1.8 |
Ventilation Shutoff
Machinery Shutdown
Electrical Isolation
Door/Damper Closure
Pre-Discharge Alarm
Piping Integrity & Leakage Test
Flow Test / Discharge Test (or simulated)
Functional Test of Detection & Release Circuitry
Interlock Verification
Cylinder Pressure & Quantity Check
Room Integrity Test (total flooding)
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Visual inspection of cylinders | Monthly |
| Control system functional test | Quarterly |
| Cylinder pressure/weight check | Semi-Annually |
| Room integrity re-verification | Annually |
| Discharge simulation | Annually |
CO₂ flooding systems are a proven, reliable, and residue-free solution for fire protection in critical applications. Proper selection between high-pressure and low-pressure systems, along with correct design, installation, commissioning, and maintenance, ensures both fire protection reliability and safety.
For design, installation, and commissioning of CO₂ flooding systems in compliance with NFPA standards,
📧 Contact us at agnirakshaniti@gmail.com.